Context-aware Telematics for UBI & Fleets
Overview
The following project is a result of acquiring a scientific grant to develop an innovative solution that adds AI-provided context to telematics. We ran a multi-phase R&D program to design and validate a contextual scoring system powered by on-device computer vision and sensor fusion, with a parallel mobile version. We built the ML pipeline, SparkSense edge device prototype, scoring algorithms, an open-map stack, and a scalable backend; then stress-tested the platform at realistic scale.
At a glance
Industry
Mobility/Telematics
Goal
Enable contextual assessment of drivers using a computer vision module and a proprietary camera device
Tech highlights
Python, TensorFlow/Keras, (YOLOv2 + classifiers), Kotlin/JVM microservices (Docker), React/React Native, Jetson Nano (edge), Firebase, open-map data

Core Business Challenge
-
Lack of context in majority of current systems: hard braking can be defensive, but today’s telematics often treat it as unsafe by default.
-
Two markets, different needs: UBI needs fair, defensible risk scores; fleets need smoothness and economy.
-
Cost & scale: device BOM target <$250; avoid high map licensing fees; handle thousands of concurrent trips.
-
Feasibility risk: many “simple” use cases require chained models and reliable sensor fusion.
Our Approach
-
Hypothesis-driven R&D: “Context improves safety and fairness” → funded by a national R&D grant.
-
Scenario first: target common crash causes (speeding, tailgating, right-of-way, crosswalks, sign compliance, lane changes) and translate them into detectable events.
-
System design: four-tier architecture (edge apps, Kotlin backend, external services, CV tier with model weights).
-
Data & experiments: built a dataset (80k images, 120h video, annotated); iterated models and fusion, then evaluated end-to-end functions, not just single models.
-
Phased delivery:
- ML feasibility + device prototyping,
- Contextual driving score (sensor + vision + maps),
- Non-functional tuning (cost, energy, reliability, scale).
- Open-map strategy: avoid per-user fees; add our own urban/limit inference and map-matching.
AI Solution
-
Edge CV pipeline (SparkSense device): Jetson Nano runs a chain of models:
- RegionProposal (segmentation)
- LaneDetection (segmentation)
- VehicleObjectDetector (YOLOv2)
- SameLaneClassifier
- TrafficLightObjectDetector
- TrafficLightColorClassifier
- RelevantLightClassifier
- PedestrianCrossingClassifier
- DistanceApproximator.
-
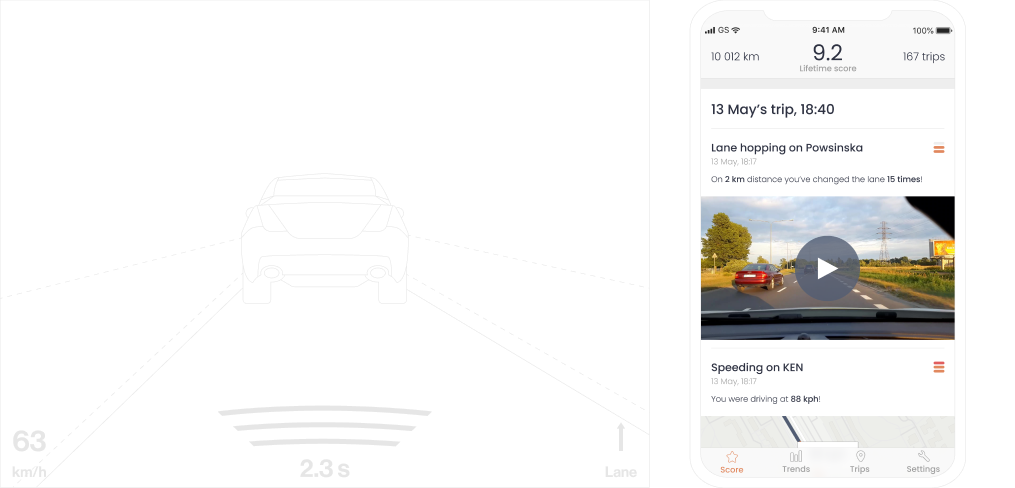
Sensor fusion adds accelerometer (IMU) and GPS; events include tailgating, red-light crossing, speeding at crosswalk, hard braking with context.
-
Driver feedback: post-trip video snippets with time/place help explain hazardous events and improve transparency.
-
Open-map augmentation - urban-area classifier and speed-limit inference reduce external map fees and improve map-matching.
-
Backend & apps - Kotlin microservices (Docker) with REST APIs; React/React Native clients; external services for notifications/object storage.
-
MLOps - evaluation harnesses per function (not just per model), fixed test sets, chained-pipeline metrics; promotion based on functional F1/precision thresholds.

Outcome
-
Perception quality: Key functions (vehicles ahead, crosswalk approach, traffic lights, tailgating distance) achieved high F1 (~0.85–0.95); more complex sequence tasks landed in the mid-0.7s to low-0.9s range.
-
Map augmentation: Urban-area inference around ~0.88 F1; speed-limit assignment ~81% exact match (baseline for further tuning).
-
Scale & reliability: Platform sustained ~8k concurrent users and ~3M requests with negligible timeouts (<0.002%).
-
Device consistency: Dual-device runs showed >90% event alignment; trip scores differed by <1 point.
-
Business impact: Context-aware scoring validated; post-trip video evidence improved transparency; open-map stack reduced recurring map fees; hardware rollout constrained by supply chain, mobile path remained viable.